How Is Raw Material Calcined In Shaft Kiln

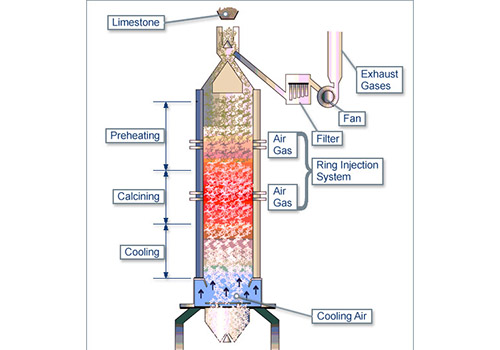
Vertical Kiln for Cement Plant
Among the many rotary kiln equipment, there is a type of kiln that is placed straight. This equipment is a vertical kiln. The working principle of this kiln is to continuously load large pieces of raw materials from the upper part, and the calcined raw materials are continuously Discharged below, the material moves from top to bottom due to gravity. The material can be divided into three sections in the kiln, namely the pre-tropical zone, the firing zone and the cooling zone. The material and the gas move in the opposite direction, so it belongs to the counterflow heat exchange device.
Temperature Control of Rotary Kiln
The temperature of the kiln in the shaft kiln is changed from 1600 degrees to 1700 degrees in the firing zone to 300-500 degrees in the feeding port. The heat of these kiln gases is used to heat the ingredients by means of radiation and convection. The values of convective and radiative heat transfer depend to a large extent on the temperature of the ingredients and gases at the junction. The temperature distribution of the kiln gas and the ingredients in the shaft kiln is generally divided into 3 cases:
The gas in the figure shows the heat capacity or water equivalent of the kiln gas stream; the W material shows the heat capacity or water equivalent of the batch. The so-called water equivalent refers to the product of the unit hour consumption and the heat capacity per unit consumption. That is, W = GC kcal / hour °C.
Verticle Shaft Kiln Advantages
When W gas > W material, the heat in the kiln gas is higher than the heat that the ingredients can absorb. Therefore, as a result of the heat exchange, the temperature of the batch can reach the initial temperature of the kiln gas, and after the heat exchange, the kiln gas has a residual temperature tk, wherein the ratio of the W gas = W material is larger, that is, the rotary kiln outlet temperature The higher tk.
When W gas = W material, the heat capacity of the kiln gas is equal to the heat that the ingredients can absorb. The kiln gas and the batch temperature are always maintained at an equal difference throughout the heat exchange process.
When W gas is used, the heat in the kiln gas is less than the heat absorbed by the ingredients. Therefore, as a result of the heat exchange, the temperature of the kiln gas is almost reduced to the initial temperature at which the shaft kiln is charged, and after the ingredients are heated, the temperature reaches tk, which is much smaller than the initial temperature t0 of the kiln gas.
It can be seen from the above 3 cases that the first and second cases are advantageous for the calcination of the shaft kiln, and the third type is not recommended for application because of the kiln cooling phenomenon.

